PAIN-FREE TREATMENT OPTIONS

Laser
Photocoagulation is a painless medical procedure used to treat internal hemorrhoids that uses a laser to create microscopic burns to seal off abnormal blood vessels or tissue. Skilled surgeons can use the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser's invisible infrared light to painlessly induce heat-driven coagulation at a specific spot in tissue. By spo
Photocoagulation is a painless medical procedure used to treat internal hemorrhoids that uses a laser to create microscopic burns to seal off abnormal blood vessels or tissue. Skilled surgeons can use the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser's invisible infrared light to painlessly induce heat-driven coagulation at a specific spot in tissue. By spot-welding internal hemorrhoidal tissue into place, laser-like welded hyper-attachments can prevent hemorrhoids from sagging downward and protruding outside the rectum. External hemorrhoids can be cosmetically reshaped with laser vaporization for a more pleasant look and feel and to make bottom hygiene easier. With a laser, there is less pain, less bleeding, and a faster recovery.
Skilled surgeons use laser light with pinpoint accuracy. The unwanted hemorrhoid is vaporized or excised. The infinitely small laser beam allows for unequaled precision and accuracy, and usually rapid, unimpeded healing. The result is less discomfort, less medication, and faster healing. A hospital stay is generally not required. The laser is inherently therapeutic, sealing off nerves and tiny blood vessels with an invisible light. By sealing superficial nerve endings, patients experience minimal postoperative discomfort. By closing tiny blood vessels, your proctologist can operate in a controlled, bloodless environment. Procedures can often be completed more quickly and with less difficulty for both patient and physician. A laser can be used alone or in combination with other modalities.
Animation of laser surgery (with comparison of hemorrhoid grades 1 to 4 on a live patient) [2:00].
Sclerotherapy
A sclerosing agent, typically 5% phenol in oil, is injected into an internal hemorrhoid. The injected substance triggers an inflammatory response; blood flow into the hemorrhoid is partially blocked, and secondary fibrosis is facilitated, shrinking and hardening the hemorrhoid.
Animation illustrating where the sclerosant is injected [0:25]. Live video showing a hemorrhoid being sclerosed [0:12].
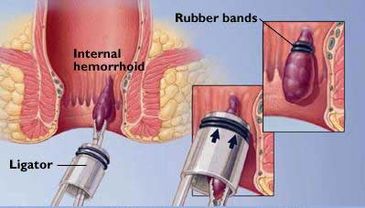
Rubber band Ligation
Rubber band Ligation
Rubber band Ligation: A grasping forceps is used to pull an internal hemorrhoid into a small one-inch tube. A rubber band is pushed off the top of the tube onto the hemorrhoid, gripping and strangulating the base of the hemorrhoid, choking off its blood supply. As a result, the hemorrhoid shrivels up and dies, and falls off during a norm
Rubber band Ligation: A grasping forceps is used to pull an internal hemorrhoid into a small one-inch tube. A rubber band is pushed off the top of the tube onto the hemorrhoid, gripping and strangulating the base of the hemorrhoid, choking off its blood supply. As a result, the hemorrhoid shrivels up and dies, and falls off during a normal bowel movement in about ten days.
Radiofrequency Coagulation

Infrared Coagulation
Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System
Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System
Infrared Coagulation (IRC) is an office-based procedure that uses heat from an intense beam of infrared light to cause the blood within the hemorrhoid to coagulate (clot). The procedure is a popular and effective alternative to surgery for small to medium-sized hemorrhoids (specifically Grade I and II). The heat creates scar tissue that
Infrared Coagulation (IRC) is an office-based procedure that uses heat from an intense beam of infrared light to cause the blood within the hemorrhoid to coagulate (clot). The procedure is a popular and effective alternative to surgery for small to medium-sized hemorrhoids (specifically Grade I and II). The heat creates scar tissue that cuts off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink, die, and eventually fall off. Scar tissue also forms on the anal canal wall, helping to anchor nearby veins in place and prevent future bulging.
IRC Educational Animation [9:15] IRC Infrared Coagulation (IRC) [0:28]

Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System
Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System
Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System
Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System: A disposable anoscope and suction band ligator are used to pull/suck the hemorrhoid into a syringe, where it is captured. Then a band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply (a variation of the ligation procedure above).
Diagnostic anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan procedure animation [4:15]

ANAL DILATION
Anoscopy and the CRH O’Regan System
ANAL DILATION
Controlled-intermittent anal dilatation is a technique that can be used to reduce hemorrhoid swelling in patients with tight anal sphincter muscles. Hemorrhoidal cushions become stretched and enlarged during regular bowel movements because more pressure is needed to defecate through a smaller, tighter sphincter. A chronic, persistent rise
Controlled-intermittent anal dilatation is a technique that can be used to reduce hemorrhoid swelling in patients with tight anal sphincter muscles. Hemorrhoidal cushions become stretched and enlarged during regular bowel movements because more pressure is needed to defecate through a smaller, tighter sphincter. A chronic, persistent rise in pressure in the lower rectum and anal canal during defecation causes permanent stretching and enlargement of the hemorrhoidal veins and other supporting connective tissues, converting normal hemorrhoidal vascular cushions into abnormal hemorrhoids. The greater the sphincter opening, the less pressure or force needed to defecate. Dilation therapy is effective for individuals with tighter muscles in the anal region to prevent the development of hemorrhoids. For more information about the effectiveness of anal dilation in the treatment of hemorrhoids, refer to the Patient satisfaction and symptom relief after anal dilatation PDF (1) below.

Hemorrhoid Energy Therapy
Hemorrhoid energy therapy (HET) is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure that uses a combination of gentle compression and low-grade heat to treat internal hemorrhoids. Performed under mild sedation, it works by minimizing blood flow and shrinking inflamed hemorrhoid tissue. The treatment uses specialized bipolar forceps and a tiss
Hemorrhoid energy therapy (HET) is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure that uses a combination of gentle compression and low-grade heat to treat internal hemorrhoids. Performed under mild sedation, it works by minimizing blood flow and shrinking inflamed hemorrhoid tissue. The treatment uses specialized bipolar forceps and a tissue temperature monitor to apply energy at a temperature between 45 and 55 degrees Celsius. HET is well tolerated, safe and highly effective in the majority of patients evaluated presenting with Grade I and II symptomatic internal hemorrhoids. For more information about how electric modalities are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids, download the Electric Treatment of Hemorrhoids PDF (2) below.

Radiofrequency Coagulation
Bipolar electrotherapy is applied for a directed coagulation effect on the mucous membrane near the hemorrhoid. A specialized Bipolar Circumactive Probe (BICAP) or a bipolar direct probe (e.g., EVRF®) is effective for the treatment of bleeding internal hemorrhoids. Bipolar electrotherapy is applied to achieve a directed coagulation/ablat
Bipolar electrotherapy is applied for a directed coagulation effect on the mucous membrane near the hemorrhoid. A specialized Bipolar Circumactive Probe (BICAP) or a bipolar direct probe (e.g., EVRF®) is effective for the treatment of bleeding internal hemorrhoids. Bipolar electrotherapy is applied to achieve a directed coagulation/ablation effect on the mucous membrane near the hemorrhoid. Caution is taken to prevent the development of a thick eschar, to avoid subsequent sloughing and delayed bleeding. For more information about how electric modalities are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids, download and view the Electric Treatment Of Hemorrhoids PDF (2) below.
Animation of EVRF Hemorrhoid Treatment [3:12]. Live video of EVRF treatment [1:47]

Hemorrhoidolysis
Hemorrhoidolysis
Hemorrhoidolysis: Negative galvanic current is sent through a needle-tipped electrode onto the surface of an internal hemorrhoid. A chemical reaction occurs around the electrode; white foam (hydrogen gas) appears, and the electrode tip becomes loose due to the liquefying action of sodium hydroxide on the proteins around the electrode. The
Hemorrhoidolysis: Negative galvanic current is sent through a needle-tipped electrode onto the surface of an internal hemorrhoid. A chemical reaction occurs around the electrode; white foam (hydrogen gas) appears, and the electrode tip becomes loose due to the liquefying action of sodium hydroxide on the proteins around the electrode. The partially liquified part of the hemorrhoid is then reabsorbed into the body's lymphatic system. For more information about how electric modalities are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids, download the Electric Treatment of Hemorrhoids PDF (2) below.
eXroid: How it Works [2:30] | Reasons for needing multiple treatments [2:12] | Ulroid Training Video [5:00] |
